3 effective breathing exercises
for autumn
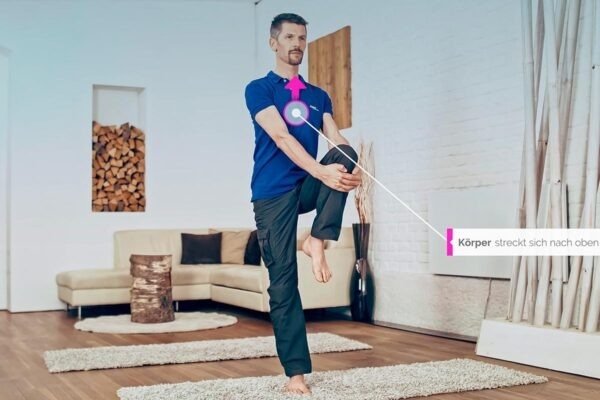
Execution
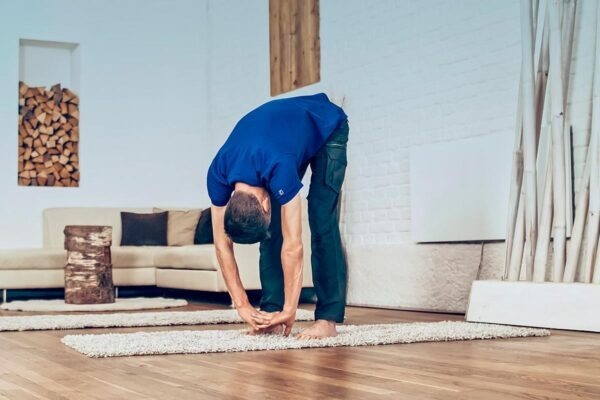
- Sit down or lie down in a comfortable position, preferably with your back straight.
- Put a hand on your belly and the other on your chest.
- Breathe through the Nose in and focus on your belly rising while your chest moves minimally.
- Breathe slowly and out through the nose in a controlled manner, gradually lowering the abdomen.
- Repeat this process several times.
Frequently asked questions
Does this exercise help with high blood pressure?
Abdominal breathing can help lower blood pressure, especially when it is due to stress or tension, this has been proven and observed time and time again.
1. stress reduction: Abdominal breathing, also called diaphragmatic breathing, promotes relaxation and stress reduction. When we are stressed, we tend to breathe shallowly and quickly, which activates the sympathetic nervous system, the part of the autonomic nervous system responsible for "fight or flight" and can increase blood pressure. By consciously using abdominal breathing, on the other hand, we activate the parasympathetic nervous system, the part of the nervous system responsible for rest and relaxation. This leads to a reduction in blood pressure.
2. oxygen supply: Abdominal breathing enables deeper and more efficient breathing. As a result, more oxygen reaches the lungs and is better distributed throughout the body. An adequate supply of oxygen helps to dilate blood vessels and lower blood pressure.
3. heart rate variability: Abdominal breathing can increase heart rate variability (HRV), which is a measure of the heart's ability to adapt to different situations. Higher HRV is often associated with a healthier cardiovascular system and lower blood pressure levels.
Execution
-
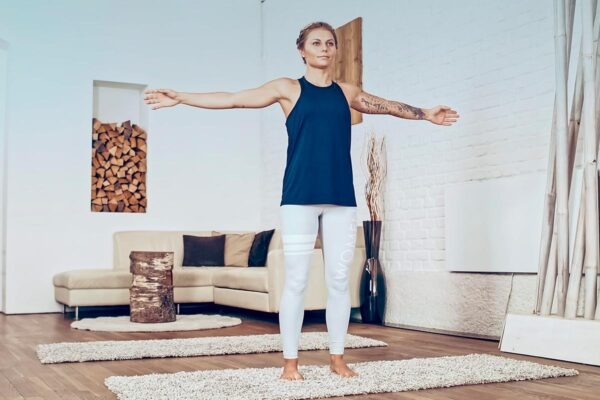
Preparation: Find a quiet and comfortable place to sit or lie down.
Gently close your eyes to minimize visual distractions. -
Start with normal breathing: First, breathe in and out normally and naturally a few times to relax.
Count every breath: -
Start counting your breaths. Each inhalation and exhalation is considered a count.
You can count the numbers internally without saying them out loud.
Goal: deepening and rest: -
As you continue the breath count, focus on gradually deepening your breathing. Try to breathe more slowly and deeply.
The goal is to relax the body and calm the mind through this deepened breathing. -
Dealing with distractions: It's normal for thoughts to pop up and distract you. When that happens, don't lose your patience.
If you notice your mind wandering or you lose count of the number of breaths, just start counting again from one without judging yourself. This is a natural part of the process. -
Duration: You can do the breath count for a set time,
z. For example, five minutes, or as long as you like.
Frequently asked questions
Does this exercise help with inner restlessness or nervousness?
Breath counting is a simple but effective breathing exercise often used to manage inner turmoil and nervousness. This technique is easy to learn and can be used in stressful situations or as a regular practice to promote relaxation.
Breath counting can be extremely helpful in stressful or nervous moments and offers the following benefits:
1. distraction from stress: Focusing on counting breaths diverts attention away from distressing thoughts or external stressors. This helps to alleviate inner turmoil.
2. calming of the mind: The repeated, conscious counting promotes relaxation of the mind. This can help reduce nervousness and find inner peace.
3. deepened breathing: Counting breaths can lead to deeper and more even breathing, which improves oxygenation and promotes physical relaxation.
4. promote mindfulness: Breath counting is a form of mindfulness practice that focuses on the present moment. This helps to detach from worries about the future or thoughts about the past.
Breath counting is a quick and effective way to calm yourself and reduce nervousness even in stressful situations. With regular practice, this simple breathing exercise can become a valuable skill for meeting the challenges of modern life with inner peace and serenity.
Become aware of your breath

Pro tip from Wolfgang
With each exhale you can let go of what you've used up, and each inhale gives you the opportunity to recharge with fresh energy. Use this opportunity as often as possible during the day.
Execution
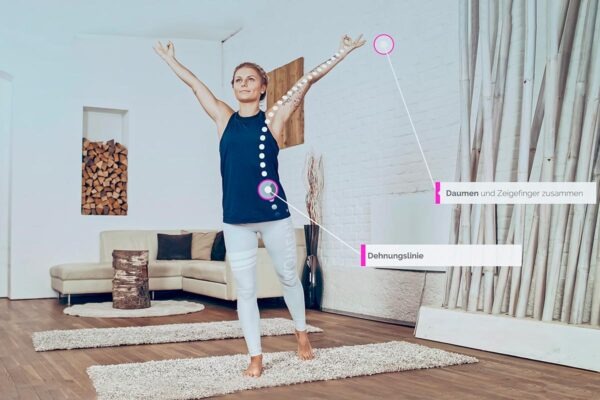
- Inhale (4 seconds): Begin by inhaling calmly and deeply through your nose while counting to four. This step is to bring fresh air and oxygen into the lungs.
- Stop (7 seconds): Hold your breath and count to seven. This step is crucial to distribute oxygen in the body and increase the concentration of carbon dioxide in the lungs.
- Exhale (8 seconds): Now exhale slowly and completely through the mouth while counting to eight. The exhalation should be gentle and even and last longer than the inhalation. Place the tongue against the upper palate behind the incisors.
- Repetition: Repeat this breathing cycle as many times as you like. You will notice that with each repetition your breathing deepens and you get into a calm and relaxed state. According to Dr. Weil, just 4 repetitions are enough to achieve a positive effect.
Advantages of the 4-7-8 breathing technique:
- Stress Reduction: The slowed breathing and deliberate concentration help lower stress levels and calm the mind.
- Sleep improvement: The 4-7-8 breathing technique is often used to relieve insomnia and fall asleep faster.
- Anxiety control: It can be useful in managing anxiety and panic attacks.
- Improving self-control: The exercise promotes self-control and supports emotional regulation.
- Improving concentration: It can increase concentration and mental clarity.
4-7-8 Breathing for relaxation and regeneration
Do you like the topic of breathing?
Then get our Meridian Yoga course and get to know your breath even better.
The course includes 34 Meridian Yoga exercises, explained in great detail, brief explanations of the exercises, 15 workouts,... And best of all:
Your own Training calendar.
This will keep you motivated.
Meridians
- Lung meridian (Yin)
11 acupuncture points
Helps with...
- Breathing problems
- Asthma
- Improves breathing
- Lung disease